AWS Cloud Practitioner Essentials
Cloud Computing is the on-demand delivery of IT services over the Internet with pay-as-you-go pricing.
Cloud deployment types:
- Cloud-based
- On-premises
- Hybrid
Benefits of the Cloud:
- Trade fixed expense for variable expense
- Benefit from massive economies of scale
- Stop guessing capacity
- Stop spending money running and mantaining data centers
- Go global in minutes
AWS global infrastructure si designed with high availability and fault rolerance in mind through the use of:
- Regions. Physical locations around the world. Contains groups of data centers called Availability Zones.
- Availability Zones (AZ). One or more data centers with redundant power, networking, and connectivity.
- Edge Locations. Data centers with low latency connection and faster delivery of content.
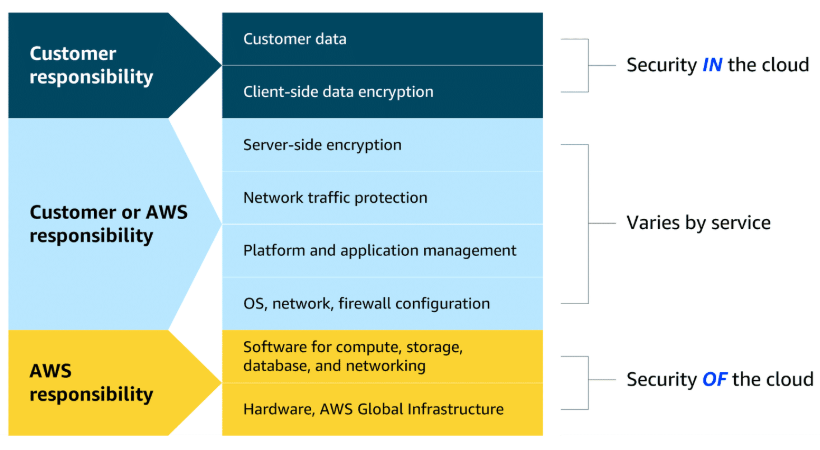
AWS Shared Responsibility Model:
Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud (EC2)
- Compute refers to the processing power needed to run applications, manage data, and perform calculations.
- Compute in the cloud means creating virtual machines with a cloud provider to run applications and tasks over the internet.
- EC2 is the cloud compute service that AWS offers.
- An EC2 instance is a VM in a physical server (multi-tenancy)
- You can choose OS and instance type (which determines CPU, memory, storage, and network performance)
- You don’t pay for stopped or terminated instances
- Instance families
- General purpose: balanced resources, web services, code repositories.
- Compute optimized: compute intensive tasks, gaming, machine learning, scientific modeling.
- Memory optimized: process of large datasets in memory, data analytics, databases.
- Accelerated computing: HW accelerators for floating point numbers calculation, graphic processing, data pattern matching, machine learning.
- Storage optimized: high performance for locally stored data such as large databases, data warehousing, intensive I/O operations.
Provision AWS resources
- Console. An interactive UI where resources can be managed
- CLI. Use of commands to manage resources
- SDK. Calling AWS APIs through the use of a progrmming language
- IaC. Infrastructure as Code, where you can define templates with the specifications for provisioning resources in differente regions in a repeatable way.
Amazon Machine Image (AMI)
- It is a pre-configured image that serves as a template for the provisioning of a AWS EC2 instance. Types:
- Custom
- Pre configured AWS AMIs
- Purchase from AWS Marketplace
AWS Pricing
- On-Demand instances: only pay for you what use
- Reserved instances: commitment for consistent instance usage
- Saving plan: commitment for consistent amount of usage
- Spot instances: temporal usage, AWS can reclaim the instance
- Dedicated host: dedicated physical server
Scaling AWS EC2
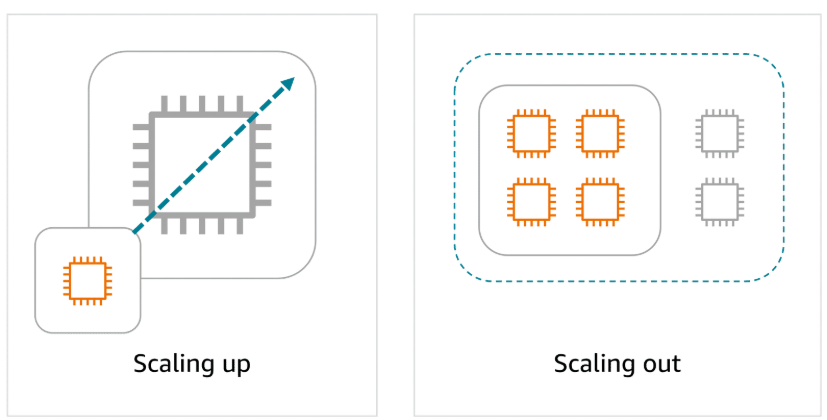
- Scalability refers to the ability of a system to handle an increased load by adding resources.
- Elasticity is the ability to automatically scale resources up or down in response to real-time demand.
- With EC2 Auto Scaling, you maintain the desired amount of compute capacity for your application by dynamically adjusting the number of EC2 instances based on demand, setting minimum, desired, and maximum capacity.
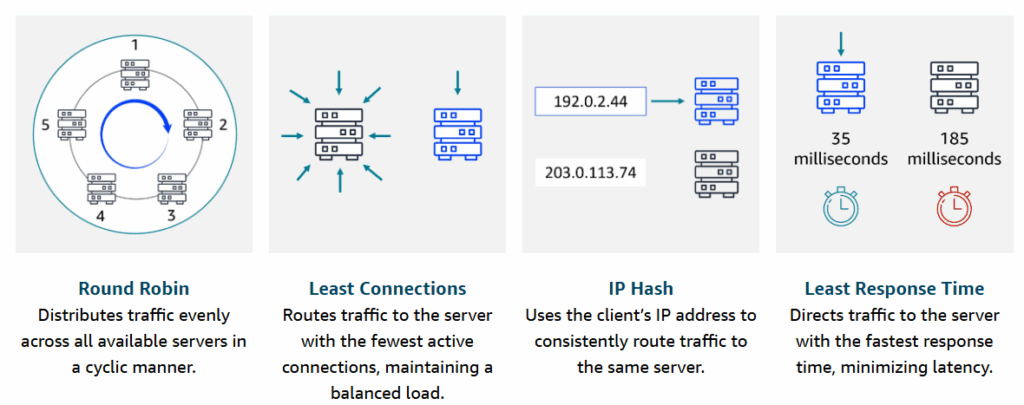
Elastic Load Balancing
Elastic Load Balancing (ELB) automatically distributes incoming application traffic across multiple resources, such as EC2 instances, to optimize performance and reliability. Some balancing methods:
EventBridge
EventBridge is a serverless service that helps connect different parts of an application using events, helping to build scalable, event-driven systems. With EventBridge, you route events from sources like custom apps, AWS services, and third-party software to other applications. EventBridge simplifies the process of receiving, filtering, transforming, and delivering events, so you can quickly build reliable applications.
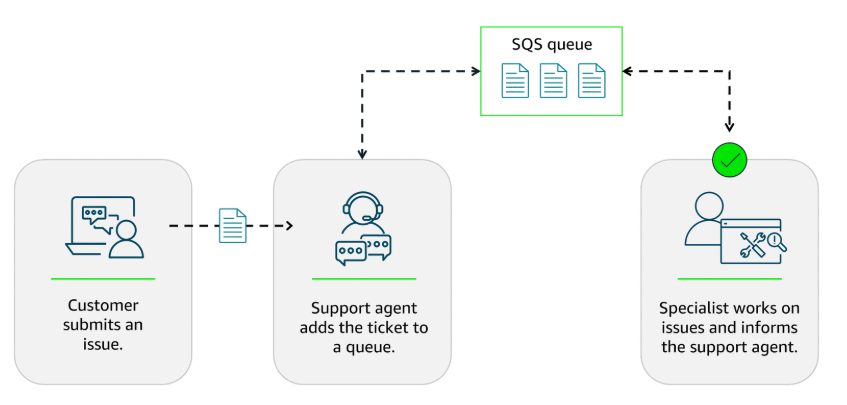
Amazon SQS (Simple Queuing Service)
Amazon SQS is a message queuing service that facilitates reliable communication between software components. It can send, store, and receive messages at any scale, making sure messages are not lost and that other services don’t need to be available for processing. In Amazon SQS, an application places messages into a queue, and a user or service retrieves the message, processes it, and then removes it from the queue.
Amazon SNS (Simple Notification Service)
Amazon SNS is a publish-subscribe service that publishers use to send messages to subscribers through SNS topics. In Amazon SNS, subscribers can include web servers, email addresses, Lambda functions, and various other endpoints.
AWS Lambda
Lambda is a serverless compute service that runs code in response to events without the need to provision or manage servers. It automatically manages the underlying infrastructure, scaling resources based on the volume of requests. You are charged only for the compute time consumed, down to the millisecond. Lambda handles execution, scaling, and resource allocation.
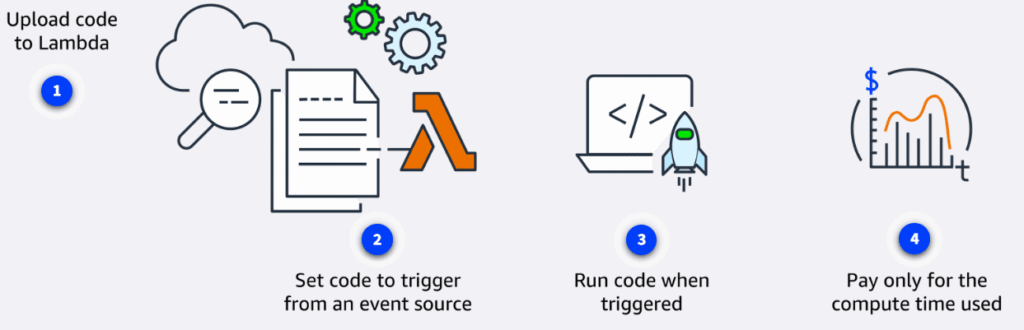
Containers and Orchestration
- Amazon ECS. Amazon Elastic Container Service (Amazon ECS) is a scalable container orchestration service for running and managing containers on AWS, like Docker containers.
- Amazon EKS. Amazon Elastic Kubernetes Service (Amazon EKS) is a fully managed service for running Kubernetes on AWS. It simplifies deploying, managing, and scaling containerized applications using open-source Kubernetes.
- Amazon ECR. Amazon Elastic Container Registry (Amazon ECR) is where you can store, manage, and deploy container images. It supports container images that follow the Open Container Initiative (OCI) standards. You can push, pull, and manage images in your Amazon ECR repositories using standard container tooling and command line interfaces (CLIs).
- Fargate. AWS Fargate is a serverless compute engine for containers. It works with both Amazon ECS and Amazon EKS. Fargate is a container hosting platform, unlike Amazon ECS and Amazon EKS, which are both container orchestration services. When using Fargate, you do not need to provision or manage servers. Fargate manages your server infrastructure for you. You can focus more on innovating and developing your applications, and you pay only for the resources that are required to run your containers.
Other Compute Services
- Elastic Beanstalk. It is a fully managed service that streamlines the deployment, management, and scaling of web applications. Developers can upload their code, and Elastic Beanstalk automatically handles the provisioning of infrastructure, scaling, load balancing, and application health monitoring. It supports various programming languages and frameworks, such as Java, .NET, Python, Node.js, Docker, and more. It provides full control over the underlying AWS resources while automating many operational tasks
- AWS Batch. It is a fully managed service that you can use to run batch computing workloads on AWS. It automatically schedules, manages, and scales compute resources for batch jobs, optimizing resource allocation based on job requirements.
- Amazon Lightsail. It is a cloud service offering virtual private servers (VPSs), storage, databases, and networking at a predictable monthly price. It’s ideal for small businesses, basic workloads, and developers seeking a straightforward AWS experience without the complexity of the full AWS Management Console.
- AWS Outposts. It is a fully managed hybrid cloud solution that extends AWS infrastructure and services to on-premises data centers. It provides a consistent experience between on premises and the AWS Cloud, offering compute, storage, and networking components.
CloudFormation
CloudFormation is a service that helps you model and set up your AWS resources so that you can spend less time managing those resources and more time focusing on your applications that run in AWS. With CloudFormation, you can define your infrastructure as code. You create a template that describes all the AWS resources that you want (like Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud (Amazon EC2) instances), and CloudFormation takes care of provisioning and configuring those resources for you.
Key considerations when choosing Regions
- Compliance. When you have to meet special requirements according to law.
- Proximity. Regios closest to your base customer reduce the latency and improves the velocity on transactions.
- Features. Not all regions have the same features, some of them have special offers that don’t exist on other regions.
- Pricing. Several factor affect the price of the services in each region, such as taxes, energy costs, etc.
Amazon VPC (Virtual Private Network)
With Amazon VPC, you can provision an isolated section of the AWS Cloud. In this isolated section, you can launch resources in a virtual network that you define. It provides three main benefits. It helps increase security because you can secure and monitor connections, screen traffic, and restrict instance access. Amazon VPC gives you full control over your resource placement, connectivity, and security. The convenience of using Amazon VPC means you will spend less time setting up, managing, and validating your virtual network when compared to on-premises network management.
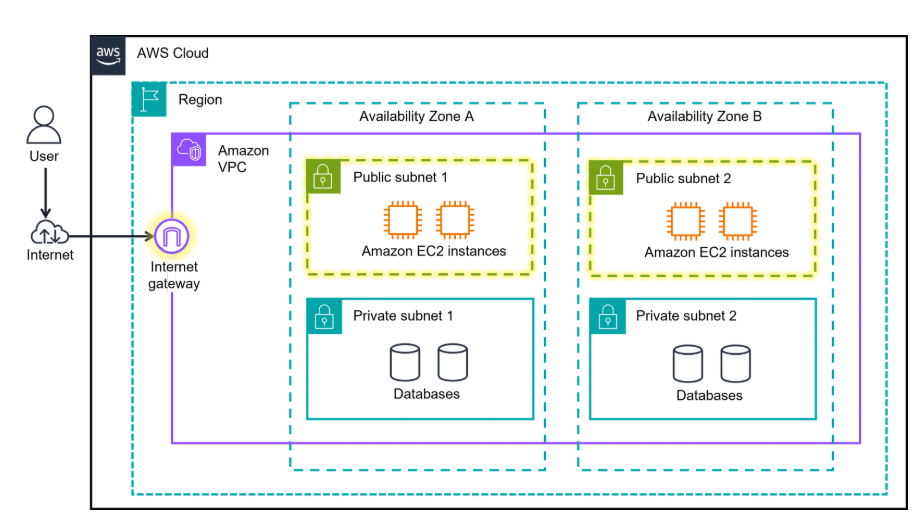

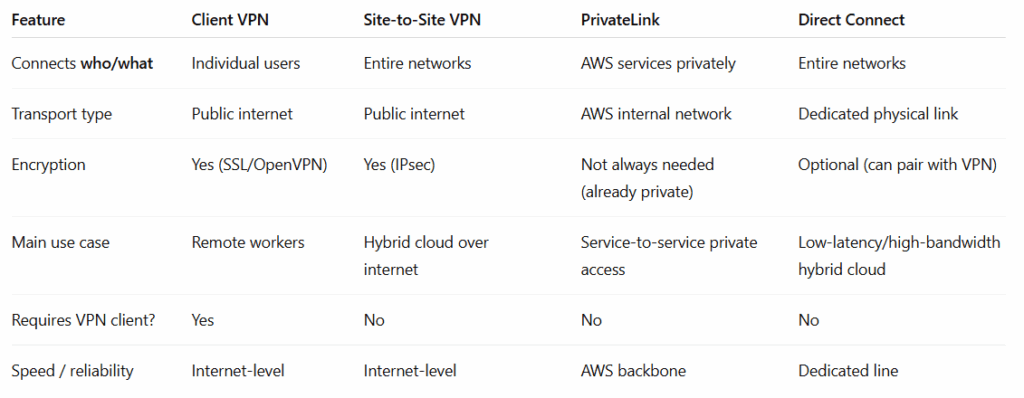
Ways to Connect to AWS